
Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
Recent smart water meter market forecasts are rosy
Several recently published research reports have been uniformly upbeat about the forecasted growth of the smart water meter market. With smart metering in the electricity and gas sectors approaching maturity, smart water meters are now expected to be the growth drivers in the smart meter market.
ABI Research, for example, predicts that double-digit growth in the smart meter market will lead to 1.2 billion connections by 2022, driven primarily by the installation of smart water meters. Although North America currently has the largest install base of smart water meters, by 2018 Europe will have that distinction. [1]
Global Market Insights expects the smart water metering market to be worth $14 billion by 2024, with 290 million new units installed during the forecast period. About 17% (50 million) of those installations will be within the context of AMI smart water management solutions. [2]
Transparency Market Research forecasts that the water meter segment will grow from a value of $3.5 billion in 2015 to $5.2 billion by the end of 2024, driven primarily by smart water meters that leverage cutting edge ultrasonic and electromagnetic technologies. [3]
As shown in the graph below, Bluefield Research foresees that $20 billion will be spent over the next decade in the US alone on smart water upgrades, with smart meters accounting for the lion’s share. [4]
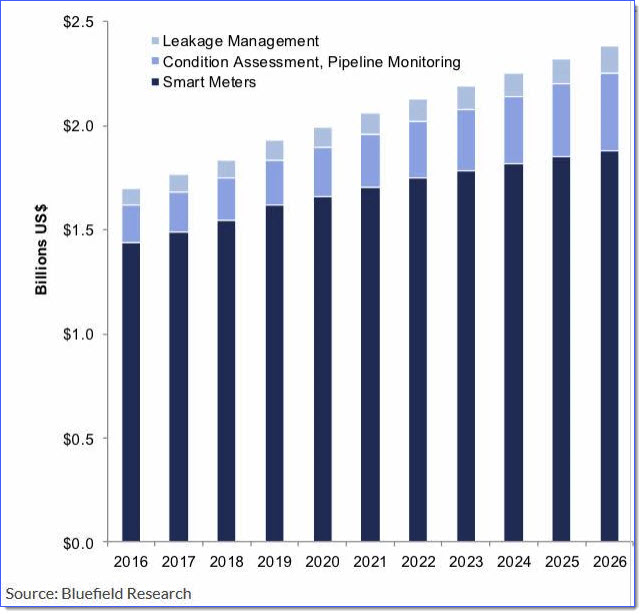
So, if it’s true that smart water meters are driving the smart meter market, then what’s driving the smart water meter market? Here are three key growth factors.
Driver 1: Technology Advances
Advances in ultrasonic and other volumetric measuring technologies are making smart water meters more precise and more reliable than ever before. But, as important as they are, smart water meters operate within holistic smart water management solutions – solutions that are being empowered by an entire range of technology advances from next-generation networks like LPWA (Low Power Wide Area) networks; to IoT machine-to-machine interfaces; to big data analytics and more.
Driver 2: Government Regulations and Investments
Population growth, accelerated urbanization and climate change are all significant stress factors on long-term water sustainability. With access to clean drinking water a basic human right, governments at all levels (national, state, municipal) set and enforce standards for water utilities. Mandated adoption of smart water meters and smart water management solutions is becoming the norm in both developed and emerging economies.
Governments are also investing in — or encouraging investment in — the infrastructures that are essential for impactful smart meter deployments. Thus, for example, the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act created the $4 billion Clean Water State Revolving Fund for projects that will repair the nation’s clean water infrastructure. And in 2012, the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology unveiled the 12th Five-Year Plan focusing on the development of intelligent grids, household and cities, including an investment of $294 billion in water resource projects. [2]
Driver 3: Operational Optimization
Smart water meters and the data that they generate provide actionable insights for water utilities about how they can optimize their water distribution operations, improve billing and consumer engagement, and reduce NRW.
But water utilities are not the only big players using smart water meters to optimize water usage. Industry accounts for 20% of water consumption worldwide. Industrial plants are also driving the adoption of smart water meters as part of their strategic goal to reduce water usage. They are not only enhancing profit margins by reducing costs, they are also strengthening their corporate citizenship profiles. The commercial smart water metering market share is expected to grow by more than 15% by 2024. [3]
A Smarter World: Smart Water Meter Sales Continue to Rise Worldwide
We decided to revisit how the market is developing and take a look at some case studies that show how the investment in smart water meters and AMI is saving money and water.
Sales and Predictions
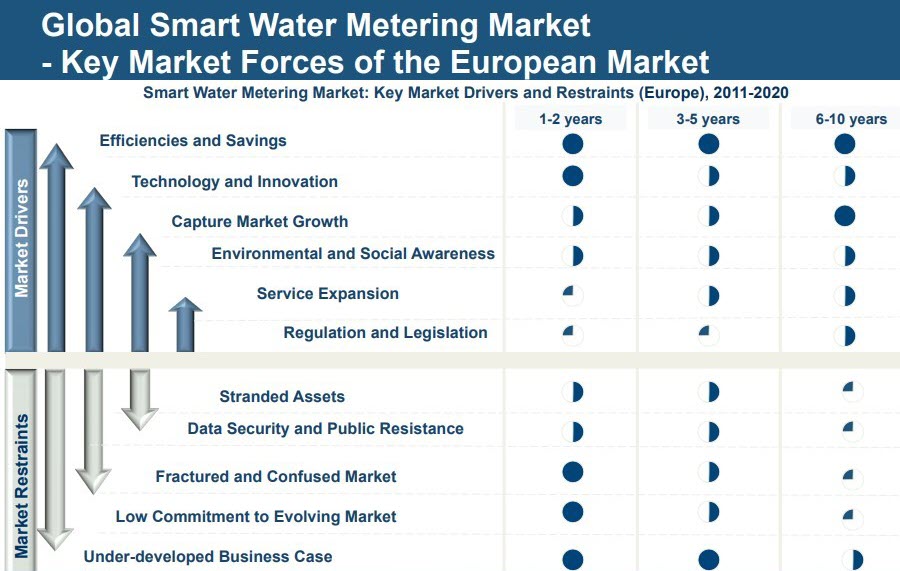
According to Frost and Sullivan, though the market share for smart
water meters is rising, the potential for sales is much higher than the actual sales today. Factors such as fear of data breaches, an under-developed business case, as well as a fractured and confused market, are constraining the actual number of sales.
As time goes by, however, these factors are expected to be mitigated, thus allowing the smart water meter market to get closer to its potential [4]
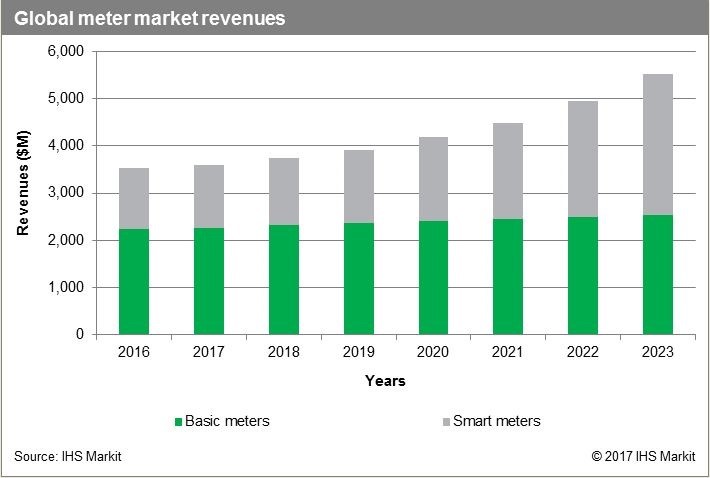
At the end of the day, the market drivers are stronger than the market constrainers. With a growing need for infrastructure maintenance, or replacement, as well as water shortages worldwide, many people are looking to smart IoT-based solutions. IHS Markit predicts that in five years’ time more than 50,000,0000 smart water meter units will be sold, about four times the sales of 2017. [5]
Studies that Make the Case for Smart Water Meters
- Due to severe drought in Western South Africa, dam levels are presently at 34%, down from 60% in 2016 and 100% in 2013. Cape Town and environs has imposed a limit of 87 liters per person per day. The problem with this solution, however, is that meters are manually read once a month and the user gets his bill two months after the meter reading. Smart meters are being brought in as an online, real-time solution whose MDM information can save the users money and Cape Town water. In addition to having individual and institutional users aware of their water consumption, the MDM system can rapidly report, leaks, burst pipes, open taps, and other problems that require immediate action. [6]
- Less than a year after installing a smart meter in the Hector Pieterson High School in Kraaifontein, a suburb of Cape Town, the school found that they saved 38,000 liters of water. Following this success and in light of the terrible drought affecting the area, it has been decided to add 100 smart water meters throughout this one school district. Members of the Educational Council are calling for all other districts to install smart waters meters to their schools. [7]
- The Bundaberg Regional Council in Queensland, Australia has voted to invest $1,000,000 in smart water meters after a heated debate. The opposing faction’s main argument is that in other Australian cities where they are using smart meters, only 20% of the people are using the information that the MDM provides. However, Bundaberg’s mayor, Jack Dempsey, argued that the average person doesn’t need to check the information, since the MDM systems proactively contact users when there is a problem. The deciding factor was that it was no longer practical to have users check their own meters. In addition to the errors, the city’s population consists of 20% pensioners for many of whom it is physically a problem to read their meters. [8]
- The Eastern Municipal Water District (EMWD) in Southern California has a three-year program that, each month, is replacing 5,000 analog water meters with smart water meters. In addition to the fact that 95% of leaks are now discovered and fixed immediately, the new program saves driving 170,000 miles a year to read meters. [9]
Final Note
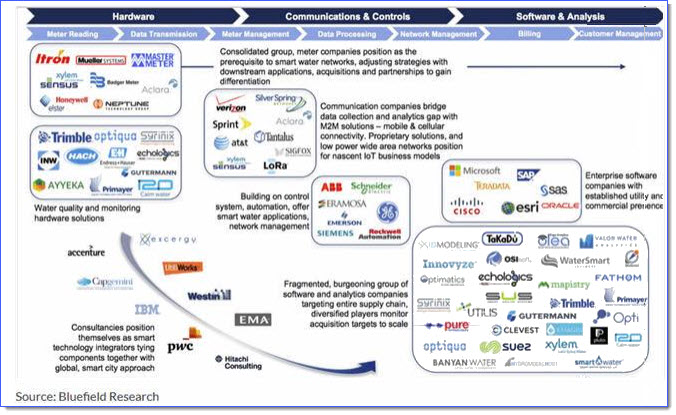
If it takes a whole village to raise a child, it takes an entire ecosystem to make water management smart. Many thanks to Bluefield Research [4] for the infographic below, which clearly shows the value chain and key stakeholders in the US smart water market. Just as a rising tide raises all boats, growth in each one of the smart water segments – from smart water meters to managed service providers – will have a positive impact on the entire market.
The world’s water experts are in agreement that smart water meters save thousands of liters of water a year and that they are essential in communities that are suffering from water shortages. All economic indicators show that as long as the cost of the meters and installation continue to be more affordable, the sales of meters will continue to rise until at least 2030.
We at the Arad Group are proud to be at the forefront of the smart water meter revolution, finding solutions for the ever growing water shortage with timely information to stop the waste of water, time and money.
References
[1] Water Utilities Drive Global Smart Meter Connection Growth to 1.2 Billion Connections in 2022,March 20, 2017
[2] Global Market Insights, Smart Water Metering Market worth $14bn by 2024, April 19, 2017
[3] Transparency Market Research, Water Meter Market: Invention of Smart Water Meter to Drive Adoption, April 21, 2017
[4] Water Online, Convergence Of Water And Data Drives $20B U.S. Smart Water Forecast, May 3, 2017
[5] Frederick Royan, Smart Water Meter Market: Global and European Perspectives, November 6, 2014
[6] Michael Markides, Smart water market will surpass $2 billion globally in 2020, December 12, 2017
[7] MJ Booyson, How smart meters can save water in drought ridden Cape Town, September 5, 2017
[8] Marvin Charles, Water Crisis: Over 100 ‘water waster’ schools to receive smart water devices, December 5, 2017
[9] Jim Alouat, $1m for water meter plan, November 1, 2017
[10] Metering and Smart Energy Int., Municipal district intensifies AMI rollout with 5,000 installations per month, August 31,2017